This update is a very special one : , this one is another (and maybe one of my favourite) rare sheep ! My Outlander Scottish Soay Sheep blend ! I have done this blend first in 2014/2015 (how time flies !!!) and is amazing to work with and super soft, so I am very very happy to be able to offer you this blend again after lots of organising, blending and dyeing. I cannot state enough that it is so important to keep rare breeds alive. It is however, harder and harder to get rare breed fibres organised for me to blend and dye them. It has taken a bit longer than normal this time, but it is so worth it and I hope you will enjoy spinning them as much as I have blending and dyeing them up for you.
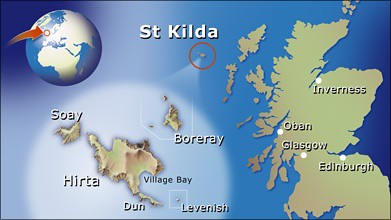
The rare sheep breed in the spot light is the very special soay sheep of the Scottish Islands of St Kilda and Hirta ! It is a very, very rare ancient breed, with roots going back all the way to the bronze age !
The Isle of Soay, a name derived from the Norse word for Sheep Island, is near the North West corner of Hirta. A very dangerous, narrow channel and sea stacks separate the two. Soay is extremely difficult to access due to its steep rocky cliffs, boulder fields and lack of anchorage.
It can only be approached when seas are very calm and quickly changing weather can make getting off the island nearly impossible, it is the least accessible of all the islands in the archipelago. It is believed that sheep have probably inhabited Soay since the Bronze Age and are the descendants of the very first domesticated sheep which populated northern Europe. They are the most primitive surviving livestock breed in the UK.
The sheep on Soay Island were not owned by the St. Kildans of Hirta, but instead by the islands various lairds (landlords). Their feudal tenants were allowed to annually collect fleece from these sheep and were occasionally permitted to take an animal, for a fee, to kill for special occasions. While Soay is somewhat larger (244 acres) than its neighbour Boreray (189 acres) Soay supports fewer animals per acre because its high central plateau is a marshy bog with little vegetation suitable to grazing sheep.
.jpg) |
| the Island of sheep |
St. Kilda is a group of islands which are the most westerly part of Scotland; they are 41 miles from Benbecula in the Outer Hebrides and 110 miles from the Scottish mainland.
This archipelago consists of four small islands and some large rocky outcrops which are all that remains of a long extinct volcano. The islands are remote and spectacular with the highest cliffs in the UK and are the home to large colonies of seabirds.
There is evidence that the main island Hirta has been inhabited for thousands of years but the habitation might not have been continuous. There is also evidence of human activity on the other three islands of Dun, Soay and the more remote Boreray.
The island of Soay has been the home of the most primitive form of domestic sheep in the UK for thousands of years which have remained as a relic of early domestication due to isolation and inaccessibility. The islanders, known as the St. Kildans were the tenants of various owners of St. Kilda, they had limited resources other than the vast seabird colonies. They caught thousands of these birds and used their feathers and extracted their oil as a currency to pay their rent and to buy meagre provisions.
The most remote island of the archipelago is Boreray which was used by the St. Kildans to harvest sea birds and their eggs and also keep a reserve flock of their unique domestic sheep, now known as Boreray Sheep.
As more communications with the mainland improved the life of the islanders changed, they were subject to diseases brought by contact with outsiders which caused heavy mortality. There was movement to the mainland and immigration to other parts of the world until in 1930 the population became so low with so few able bodied men they could no longer sustain themselves and they chose to leave. In 1957, the entire archipelago was bequeathed to the National Trust for Scotland and has been in their ownership and protection ever since.
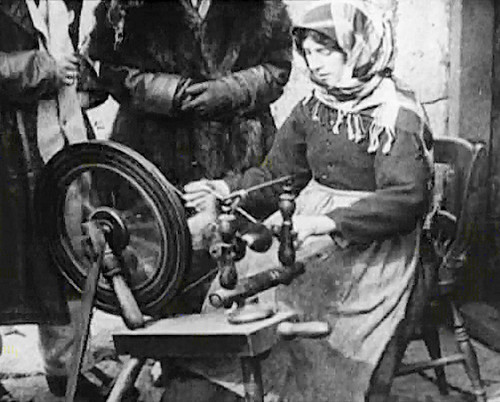
 |
 |
| Tourists flocking around a spinner showing them spinning soay (1900s) |
 |
| close up |
 |
| spinning magic |
 |
| now the same street is deserted... except for the grazing soay sheep that have been there for centuries |
The animals on Soay have never been managed and lived feral on the island for thousands of years, no one is certain how long or how they got there.
There are dark and blond sheep with some ewes being horned and many others polled (no horns) or scurred (small or misshaped horns). Over recent centuries some animals have been taken from Soay to estates on the mainland of the UK. Over a period of time starting in 1932, after St. Kilda had been evacuated and sold, 107 animals were captured and transferred to the vacant pastures of Hirta.
This was a significant number taken from the small population on Soay Island. Today flocks survive in both locations.
Visitors to St Kilda will immediately notice three striking features of the sheep.
First, Soay sheep are tiny. In August, mature females average around 24kg in weight while mature males are around 38kg, making them about one third the size of most modern domestic sheep and shrinking !
Second, they are highly variable in appearance. While many Soays have the ‘classic’ Soay coat colour, which we call ‘dark wild’ (with ‘wild’ being short for ‘wildtype’ the coat pattern that features a light belly and rump patch), we recognise three other varieties (‘dark self’, ‘light wild(type)’ and ‘light self’ (where ‘self’ refers to ‘self-coloured’ – a coat pattern with the same colour all over including belly and rump patch).
Studies have shown that the dark/light colouration is due to a gene called tyrosinase-related protein 1, or TYRP1 which is on sheep chromosome 2 and genetically dark is dominant to light, while the wild/self colouration is due to the locus Agouti on sheep chromosome 13 and wild is dominant to self.
There are however, very cute Soay sheep with white patches as well. (note: in angora rabbits for example there is the agouti on chromosome 13 as well, making the off spring able to have all different colours. Agouti is a gorgeous thing to have in the gene pool !).
Studies have shown that the dark/light colouration is due to a gene called tyrosinase-related protein 1, or TYRP1 which is on sheep chromosome 2 and genetically dark is dominant to light, while the wild/self colouration is due to the locus Agouti on sheep chromosome 13 and wild is dominant to self.
There are however, very cute Soay sheep with white patches as well. (note: in angora rabbits for example there is the agouti on chromosome 13 as well, making the off spring able to have all different colours. Agouti is a gorgeous thing to have in the gene pool !).
 |
The University of Edinburg is doing a lot of research on these soay sheep because it offers them a very good insight in the ecology and the evolution of the species. A count of the whole of Hirta’s Soay sheep population has been conducted most years since 1952 by the same method.
It was these counts that revealed that Soay sheep on St Kilda have rather unusual population dynamics. The Soay population rises to maxima and then crashes, at irregular intervals. It is this population dynamic behaviour that makes Soay sheep so interesting for ecologists. The sheep exhibit a phenomenon known as overcompensatory density dependence, in which their population never reaches equilibrium.
The population growth is so great as to exceed the carrying capacity of the island, which eventually causes a dramatic population crash, and then the cycle repeats. For example, in 1989, the population fell by two thirds within 12 weeks !!
In brief, it became clear that the population dynamics of Soay sheep happen because virtually all mature females conceive each year, regardless of density, and as a result, the population can increase in one breeding season to a size which greatly exceeds the winter carrying capacity, when it may crash. Crashes are more likely to occur when there is bad winter weather, and when the population contains a large proportion of vulnerable sheep such as lambs and males. The population then increases again, over several years, before another crash.
As ecological research proceeded, it became clear that the Soay sheep population also offers remarkable opportunities for understanding the progress of natural selection and evolution in real time. Population crashes are a period of intense selection, could they have anything to do with the maintenance of genetic variation, for example in coat colour and horn type? Does the low life expectancy of most individuals select for early reproductive effort? Likewise, the population dynamics research inspires numerous questions about the relationship between the sheep and their biotic environment, including the plants on which they feed and the parasites.
The Soay sheep have short tails and naturally shed their wool, which can be hand plucked (called rooing) in the spring and early summer. About one kilogram of wool can be obtained from each animal per year.
It was these counts that revealed that Soay sheep on St Kilda have rather unusual population dynamics. The Soay population rises to maxima and then crashes, at irregular intervals. It is this population dynamic behaviour that makes Soay sheep so interesting for ecologists. The sheep exhibit a phenomenon known as overcompensatory density dependence, in which their population never reaches equilibrium.
The population growth is so great as to exceed the carrying capacity of the island, which eventually causes a dramatic population crash, and then the cycle repeats. For example, in 1989, the population fell by two thirds within 12 weeks !!
In brief, it became clear that the population dynamics of Soay sheep happen because virtually all mature females conceive each year, regardless of density, and as a result, the population can increase in one breeding season to a size which greatly exceeds the winter carrying capacity, when it may crash. Crashes are more likely to occur when there is bad winter weather, and when the population contains a large proportion of vulnerable sheep such as lambs and males. The population then increases again, over several years, before another crash.
As ecological research proceeded, it became clear that the Soay sheep population also offers remarkable opportunities for understanding the progress of natural selection and evolution in real time. Population crashes are a period of intense selection, could they have anything to do with the maintenance of genetic variation, for example in coat colour and horn type? Does the low life expectancy of most individuals select for early reproductive effort? Likewise, the population dynamics research inspires numerous questions about the relationship between the sheep and their biotic environment, including the plants on which they feed and the parasites.
The Soay sheep have short tails and naturally shed their wool, which can be hand plucked (called rooing) in the spring and early summer. About one kilogram of wool can be obtained from each animal per year.
 |
This breed has extremely fine fleece and it is difficult to distinguish an outer coat. This is a clear indication that the Soay are indeed the product of a domesticated breed in prehistoric times.
The breed also lacks the flocking instinct of many breeds. Attempts to work them using sheep dogs result in a scattering of the group: no use entering them at the Bendigo sheep and wool show dog trials: it would be extremely frustrating for the sheep and dogs. They obviously are the rebels among sheep !
The breed also lacks the flocking instinct of many breeds. Attempts to work them using sheep dogs result in a scattering of the group: no use entering them at the Bendigo sheep and wool show dog trials: it would be extremely frustrating for the sheep and dogs. They obviously are the rebels among sheep !
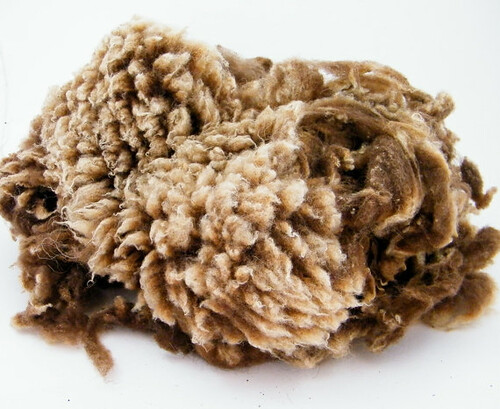 |
| Soay sheep fleece |
These sheep are extremely special and it inspired me to do a rare sheep breed adventure blend named OUTLANDER, hence its name , because I am a fan of the books and the series…and because the Soay sheep , although hairier, are pretty darn cute. I have some naked Outlander tops as well and then there are all the different colourways, fresh out of the dyepots this week available as well
have fun exploring the Outlander tops this week!
happy spinning and crafting !
You can find all the new Outlander tops here on the IxCHeL online shop: https://ixchel.com.au/products/outlander
big hugs
Charly




No comments:
Post a Comment